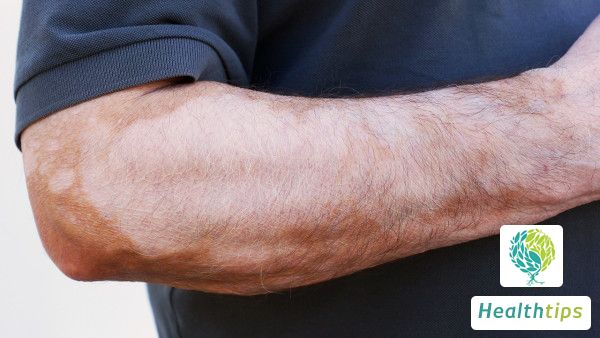
Vitiligo is a common acquired depigmentation disease of skin and mucous membranes that can occur anywhere on the body. Its cause is still unclear and may be related to factors such as heredity and autoimmune function. The clinical manifestations of vitiligo are white spots or white hair, mostly without conscious symptoms, and a few patients may have local itching sensation in the affected area before or at the same time of onset. Vitiligo often occurs in exposed and friction-prone areas such as the face, neck, and back of the hand. It is generally believed that the occurrence of vitiligo is related to the following factors: 1. Heredity: Vitiligo has a certain family clustering, and if both or one of the parents has vitiligo, the probability of their children developing vitiligo will increase; 2. Mental factors: People who are constantly under stress or anxiety are prone to vitiligo, because the function of melanocytes in their bodies is impaired, leading to impaired melanin synthesis and inducing vitiligo; 3. Trauma: Including burns, sunburns, etc. If the skin is injured, it may lead to the destruction of melanocytes in the skin, thereby causing vitiligo; 4. Endocrine disorders: Some female patients may experience endocrine disorders during pregnancy or lactation, and vitiligo is also prone to occur at this time; 5. Others: For example, exposure to chemical substances, sun exposure, etc., can also induce vitiligo. It is recommended that patients pay attention to sun protection and avoid ultraviolet exposure. In terms of diet, they can properly eat foods rich in vitamin C, such as kiwi and oranges.