What Can a CT Scan Detect?
The diseases that can be detected through CT scans include intracranial tumors, abscesses, and other central nervous system diseases, respiratory diseases such as pneumonia and tuberculosis, circulatory system diseases such as coronary artery disease and myocardial disease, as well as skeletal and muscular system diseases and digestive system diseases.

CT scans of the central nervous system have high diagnostic value, especially for intracranial tumors, abscesses, granulomas, parasitic diseases, craniocerebral trauma, hematomas, hemorrhages, cerebral infarction, congenital malformations or dysplasia, intraspinal tumors, spinal stenosis, and vertebral disc herniation. However, it should be noted that CT scans have certain limitations in the diagnosis of vascular malformations.
CT scans of the respiratory system are frequently used, especially for the detection of tracheal and bronchial diseases, congenital lung diseases, pneumonia, tuberculosis, lung fungal diseases, and lung tumors such as lung cancer. Low-dose spiral CT is the preferred method for screening lung cancer (right upper lung cancer).
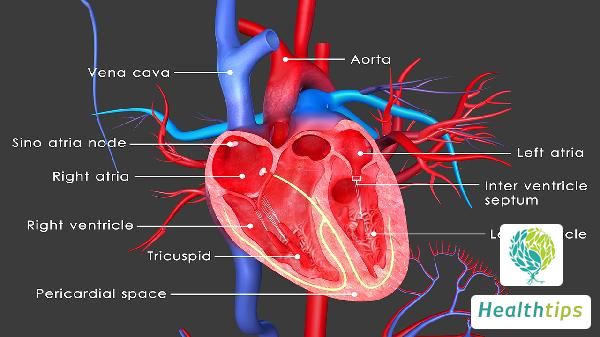
CT scans of the circulatory system are mainly used for the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases, aortic aneurysms, coronary artery disease, myocardial disease, etc. One of the most common applications is the use of stents in the coronary arteries.
CT scans of the skeletal and muscular system are often used to detect fractures, joint dislocations, osteomyelitis, osteoarticular tuberculosis, and bone tumors. They can also be used to detect spinal lesions and soft tissue lesions, but their diagnostic accuracy is not as good as MRI.
There are some specific points to note when performing CT scans of the digestive system. Solid organs such as the spleen, liver, and pancreas can be well visualized with CT scans, and the sensitivity and diagnostic accuracy are relatively high. However, the sensitivity of CT scans for hollow organs such as the gastrointestinal tract and bile ducts is relatively poor, and it is not as effective as endoscopy or other methods.