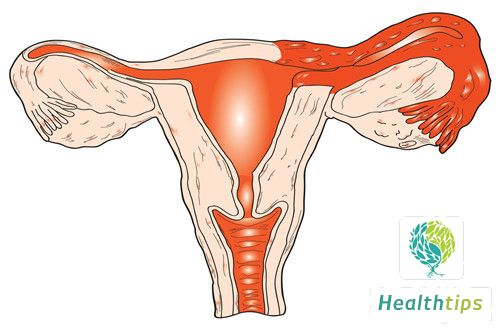
Female reproductive organs include the fallopian tube, which is an internal reproductive organ. The fallopian tube is where sperm and eggs combine, and it also has the function of transporting the fertilized egg to the uterine cavity. Typically, the fallopian tube has a length of 8-14cm. It is a muscular tissue with an internal connection to the uterine cavity and an external portion, the fimbria, located in the abdominal cavity.
How Long After Fallopian Tube Flushing Can Pregnancy Occur? It depends on the type of fluid used for the flushing. If the fluid is harmless, pregnancy can be considered the following month. However, flushing is not always recommended. If imaging tests confirm that the fallopian tubes are patent, there is no need for further flushing. Fluoroscopy using iodinated oil can sometimes have a therapeutic effect on inflammation in the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes. Flushing has limited therapeutic benefits and can potentially introduce external bacteria during the procedure, so it is not always advisable.
Some medical institutions may still perform flushing, but it is not unconditionally opposed. If imaging tests confirm patent fallopian tubes, other methods can be considered to address other issues.
What Are Fallopian Tubes? Fallopian tubes are part of the female reproductive organs and belong to the internal reproductive system. They are the site where sperm and eggs combine and have the function of transporting the fertilized egg to the uterine cavity. Typically, they have a length of 8-14cm. The fallopian tubes are muscular tissues with an internal connection to the uterine cavity and an external fimbria located in the abdominal cavity. From the inside out, they are divided into four main parts: the interstitial part, the isthmus, the ampulla, and the fimbria. Each part has different functions. The fimbria mainly functions to pick up eggs, while the ampulla is the main site of fertilization.
Some people may ask about the location for tubal ligation if it is necessary. Typically, it is performed between the ampulla and the isthmus, as well as in the interstitial part. This area is usually only about 1 centimeter long and relatively narrow. If an ectopic pregnancy occurs in this area, it can be relatively weak and prone to rupture, which can result in significant bleeding.
Please note that these are general explanations, and specific medical advice should be obtained from a qualified healthcare provider.




















