First, an ultrasound examination should be performed to determine the location of the placenta and the condition of the fetus. Select the needle insertion point, sterilize the skin, spread the sterile sheet, and perform local anesthesia. Then, use a lumbar puncture needle with a needle core to puncture at the puncture point. When amniotic fluid is withdrawn, it proves that the puncture is successful. After the puncture, you need to rest in a supine position for half an hour. If symptoms such as chest tightness and shortness of breath occur, they should be treated promptly.
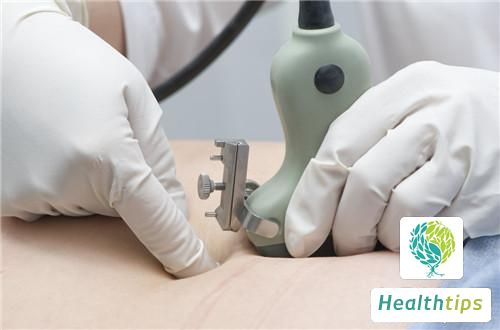
1. Before officially extracting amniotic fluid, an ultrasound examination should be performed first to determine the size of the fetus, gestational age, fetal position, and number of fetuses, and find the most suitable position for needle insertion.
2. Before undergoing amniotic fluid puncture, the pregnant woman should lie flat on the bed and continuously rotate her body five times, which can suspend the fetal cells in the amniotic fluid in the pregnant woman's body, making it easier to extract fetal cells, simplifying the examination process, and making the examination results more obvious.
3. After deciding on the needle insertion position, sterilize the pregnant woman's skin and spread a sterile sheet over her abdomen.
4. Under the guidance of ultrasound, use a 20 or 22 gauge spinal puncture needle to gradually puncture into the amniotic cavity that was previously selected.
5. Use the puncture needle to puncture at the puncture site, withdraw about 28 milliliters of amniotic fluid, inject it into a sterile centrifuge tube, and then seal the centrifuge tube with a sterile seal.
6. Evenly distribute the suspension for cell culture and place it in a culture flask. After sterile sealing, place the culture flask under a microscope to observe its growth. After culturing for about half a month, cells can be obtained for chromosome analysis.

