If a wound becomes rotten, it is important to promptly seek medical attention for debridement and disinfection. Take anti-inflammatory medication under the guidance of a doctor to prevent inflammation. It is also necessary to keep the wound clean and dry, avoiding contact with water too early, as this may affect the healing process. Do not attempt to treat rotten wounds yourself, as this can easily lead to worsening symptoms.
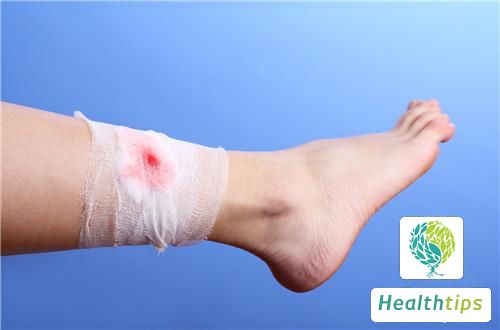 Mild cases of wound rot can be treated by flushing the wound with normal saline, disinfecting it with iodophor, and finally dressing it with medical gauze. The patient should maintain cleanliness and dryness of the affected area and avoid contact with water to prevent infection.
In more severe cases of wound rot, where there is extensive tissue necrosis, the necrotic tissue should be removed first, followed by disinfection of the affected area. After disinfection, anti-inflammatory and analgesic medication can be applied, and the wound should be dressed. If the wound is large, anesthetics can be used during the removal of necrotic tissue to reduce patient discomfort.
When wound rot occurs, a bacterial culture and drug sensitivity test can be performed on a sample of the affected area's secretions. Based on the results, appropriate antibiotics can be selected for anti-infective treatment, which can further enhance the treatment effect and shorten the duration of illness. If the patient experiences severe pain due to the ulcerated wound, they can take analgesic medication or receive intravenous injection under the guidance of a doctor to relieve the pain.
Mild cases of wound rot can be treated by flushing the wound with normal saline, disinfecting it with iodophor, and finally dressing it with medical gauze. The patient should maintain cleanliness and dryness of the affected area and avoid contact with water to prevent infection.
In more severe cases of wound rot, where there is extensive tissue necrosis, the necrotic tissue should be removed first, followed by disinfection of the affected area. After disinfection, anti-inflammatory and analgesic medication can be applied, and the wound should be dressed. If the wound is large, anesthetics can be used during the removal of necrotic tissue to reduce patient discomfort.
When wound rot occurs, a bacterial culture and drug sensitivity test can be performed on a sample of the affected area's secretions. Based on the results, appropriate antibiotics can be selected for anti-infective treatment, which can further enhance the treatment effect and shorten the duration of illness. If the patient experiences severe pain due to the ulcerated wound, they can take analgesic medication or receive intravenous injection under the guidance of a doctor to relieve the pain.




















