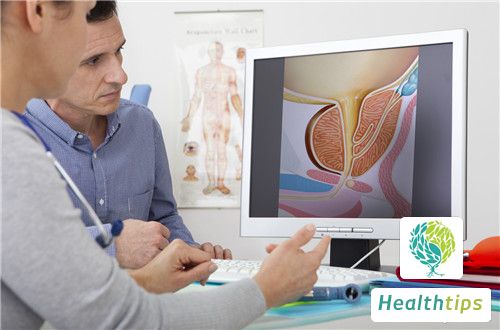
The prostate is the largest gland in the male reproductive glands, participating in semen synthesis, promoting male sexual development, and regulating endocrine. The male prostate is composed of prostatic tissue and muscle tissue. When the prostate is diseased, it will affect the quality of semen, and severe cases may cause infertility. Common prostatic diseases include prostatitis and prostatic hyperplasia. What is the male prostate? The prostate is an important gland in the male urinary reproductive tract. The prostate is shaped like an inverted chestnut, with its proximal end connected to the bladder neck and its distal end connected to the urethral membrane. The entire posterior urethra passes through the middle of the prostate. In addition, the prostate has an abdominal opening, which is one of the channels for semen ejection. The main function of the prostate is to secrete prostatic fluid, which is an important component of male semen, accounting for about 30% of the total semen volume. The prostatic fluid contains liquefaction factors of semen, and the semen ejected from the body needs to be liquefied with the help of the liquefaction factors of prostatic fluid. When the prostate is diseased, it is easy to cause semen not to liquefy, which may lead to infertility and other conditions. Common clinical diseases include chronic prostatitis and prostatic hyperplasia. The prostate participates in the semen process, secreting a variety of secretions, which are very important components of semen. Among them, the prostatic fluid accounts for about 30% of the total semen volume. Therefore, the male prostate also provides a very good environment for sperm, allowing sperm to flow freely and entering the uterus to create a very good condition. Promoting male sexual development, the male prostate can quickly metabolize testosterone in the human body into male hormones, which are also very important and can stimulate male sexual development and male reproductive development. Regulating body endocrine, the male prostate secretes a variety of enzymes, such as amylase, protease, etc., and can also regulate trace elements such as calcium and iron in the body, which has a very good function for regulating human endocrine.