The location of the female bladder inside the human body is in the pelvis, below the uterus, in front of the vagina, and in the lower part of the abdomen. When there is no excretion in the bladder, most of it is behind the pubic symphysis. When the bladder is full of urine, it will expand upwards to the position of the navel, and you will feel bulging when you touch it with your hand.
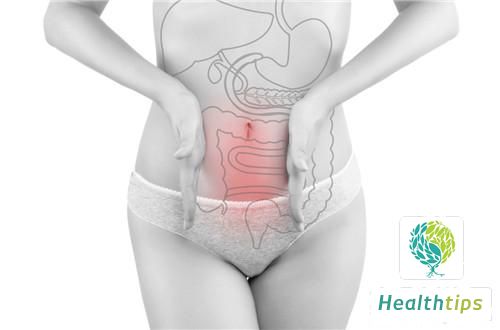
1. If women have pain in the bladder area, it is more likely to be caused by cystitis. The occurrence of cystitis is related to bacterial retrograde infection, which can invade the inner mucosa of the bladder, causing pain and other discomfort, and some women may also experience discomfort in the perineum.
2. Due to physiological structure, women's urethra is shorter and thicker, which is prone to bacterial retrograde infection, leading to bladder inflammation. Women should pay attention to drinking more water, not holding back urine, and also strengthening their bodies, which can reduce the incidence of cystitis.
3. In addition, it should be noted that female bladder cancer is more easily overlooked because women are more prone to urethritis, which can cause frequent urination and pain, possibly masking some early symptoms of bladder cancer.
4. The early symptoms of female bladder cancer mainly manifest as frequent urination, hematuria, and urinary pain. These symptoms must be differentiated from cystitis or urethritis. However, urethritis rarely causes hematuria, especially visible hematuria, and cystitis rarely causes hematuria. Therefore, once there is hematuria, it must be taken seriously.

