The lungs are an important organ that constitutes the human respiratory system. However, if a person lives or works in a heavily polluted environment for a long time, they are prone to developing lung diseases. For instance, in the past, many miners were prone to developing pneumoconiosis due to inadequate protective measures and prolonged exposure. If you suspect that you may have a lung disease, it is recommended to promptly visit a hospital for a lung examination. So, what does pulmonary fibrous proliferative lesion represent?
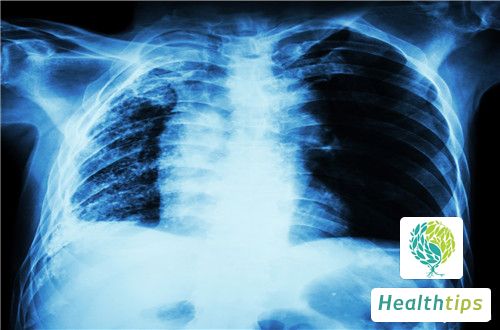 1. Exudative lesions: When the immune system is weak, the number of bacteria is high and virulent, or the allergic reaction is strong, a blurred, cloudy, and patchy shadow can be seen on the chest X-ray.
2. Proliferative lesions: When the number of bacteria is low, the virulence is weak, or the body's resistance is strong, roundish nodule shadows with a diameter of 4 to 10 millimeters and clear boundaries can be seen on the chest X-ray.
3. Caseous lesions: When there is a large number of virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis, low body resistance, or enhanced allergic reactions, lung tissue necrosis and liquefaction occur, and necrotic material is expelled through the bronchi. Thick-walled cavities can often be seen on the chest X-ray.
4. Fibrosis lesions: After the healing of the above-mentioned exudative, proliferative, and caseous lesions, linear, reticular, or stellate fibrous strands can be seen on the chest X-ray. This is the main manifestation of adult tuberculosis healing.
5. Calcification manifests as high-density, irregular shadows with sharp boundaries on the chest X-ray. This is the main manifestation of childhood tuberculosis healing.
6. Lung infection: Lung fibrosis lesions are generally due to lung infections in the body, which leave fibrotic lesions after natural healing. The cause is generally a normal manifestation of repair after the healing of tuberculosis or other inflammatory injuries. If the scope of fibrosis is small, it will not have any impact on the body and does not require treatment. However, if the scope increases, it can easily lead to reduced lung function, hypoxia, and difficulty breathing. Regular observation of lung function changes is recommended, especially when there is repeated stimulating cough, coughing up mucus, or blood in the mucus, it is necessary to undergo examination. Avoid smoking and drinking, breathe fresh air appropriately, and exercise regularly to enhance the body's resistance and immunity.
1. Exudative lesions: When the immune system is weak, the number of bacteria is high and virulent, or the allergic reaction is strong, a blurred, cloudy, and patchy shadow can be seen on the chest X-ray.
2. Proliferative lesions: When the number of bacteria is low, the virulence is weak, or the body's resistance is strong, roundish nodule shadows with a diameter of 4 to 10 millimeters and clear boundaries can be seen on the chest X-ray.
3. Caseous lesions: When there is a large number of virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis, low body resistance, or enhanced allergic reactions, lung tissue necrosis and liquefaction occur, and necrotic material is expelled through the bronchi. Thick-walled cavities can often be seen on the chest X-ray.
4. Fibrosis lesions: After the healing of the above-mentioned exudative, proliferative, and caseous lesions, linear, reticular, or stellate fibrous strands can be seen on the chest X-ray. This is the main manifestation of adult tuberculosis healing.
5. Calcification manifests as high-density, irregular shadows with sharp boundaries on the chest X-ray. This is the main manifestation of childhood tuberculosis healing.
6. Lung infection: Lung fibrosis lesions are generally due to lung infections in the body, which leave fibrotic lesions after natural healing. The cause is generally a normal manifestation of repair after the healing of tuberculosis or other inflammatory injuries. If the scope of fibrosis is small, it will not have any impact on the body and does not require treatment. However, if the scope increases, it can easily lead to reduced lung function, hypoxia, and difficulty breathing. Regular observation of lung function changes is recommended, especially when there is repeated stimulating cough, coughing up mucus, or blood in the mucus, it is necessary to undergo examination. Avoid smoking and drinking, breathe fresh air appropriately, and exercise regularly to enhance the body's resistance and immunity.




















