What are the specific medications for treating rectitis?
For example, ulcerative rectitis is often treated with medications such as 5-aminosalicylic acid preparations and methylprednisolone; radiation rectitis can be improved with sucralfate and cottonseed oil; and infectious rectitis can be treated with levofloxacin or acyclovir. Surgical treatment may be performed by a doctor if necessary.
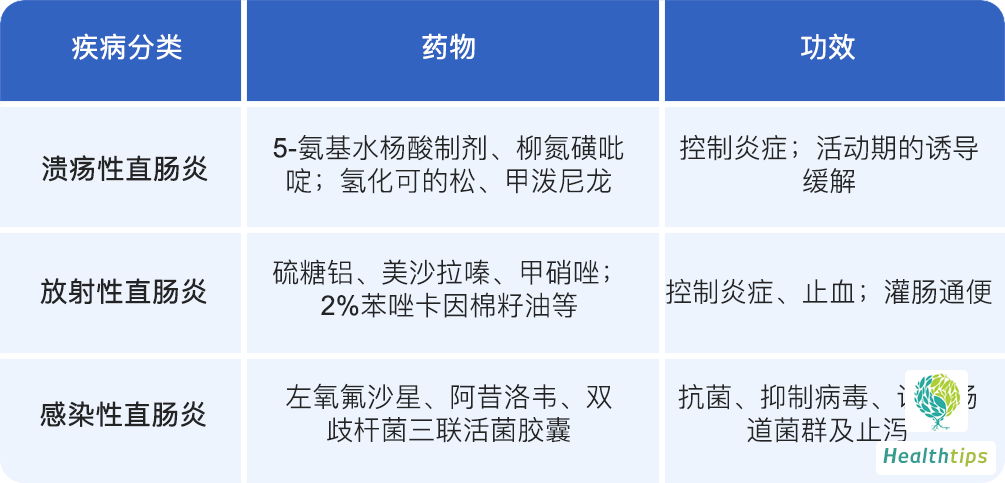
Ulcerative rectitis can usually be controlled with 5-aminosalicylic acid preparations and sulfasalazine to reduce inflammatory responses. For moderate to severe patients with poor response to 5-aminosalicylic acid preparations, glucocorticoids such as hydrocortisone and methylprednisolone are the preferred treatment. Glucocorticoids are only used for induction of remission during the active phase and should be gradually reduced and discontinued after symptom control, as long-term use is not recommended.
Severe radiation rectitis can lead to bleeding and pain, and can be treated with medications such as sucralfate, mesalazine, and metronidazole to help control intestinal inflammation and reduce intestinal bleeding. Additionally, 2% benzocaine cottonseed oil enemas, warm paraffin oil enemas, or warm water baths can be used to help open intestinal obstruction.
If infectious rectitis is caused by bacterial infection, treatment should target the pathogen, usually requiring antibiotics such as levofloxacin. For viral infections, antiviral drugs such as acyclovir can be used. Meanwhile, bifidobacterium triple viable capsule can improve diarrhea caused by intestinal flora imbalance due to enteritis.



















